
Computer viruses cannot be described in several words. There are tens of types and subtypes of them, and each has many unique characteristics. Describing them all can take hours or even days – but I tried to make a short comprehension of each type. This information will be useful for everyone who has a computer and uses it every day.
But first, let me answer a single question. What is a computer virus? A computer virus is an umbrella term for malicious software. However, such a definition is not 100% correct. Malicious software, or malware, is a class of programs designed to make money on their victims or just to mischief the users who got one. And originally, viruses were just malware – and not a common term. You can read more general information in a separate article, but we will review only computer virus types there.
How many types of computer viruses are there?
It is hard to give a correct answer. Many different computer viruses appear each day, and a certain amount turns inactive. Even if we look at the most active ones, we will struggle to count them all without missing something. So, let’s tamper the circle and look only at general types – there are still more than 10 of them.
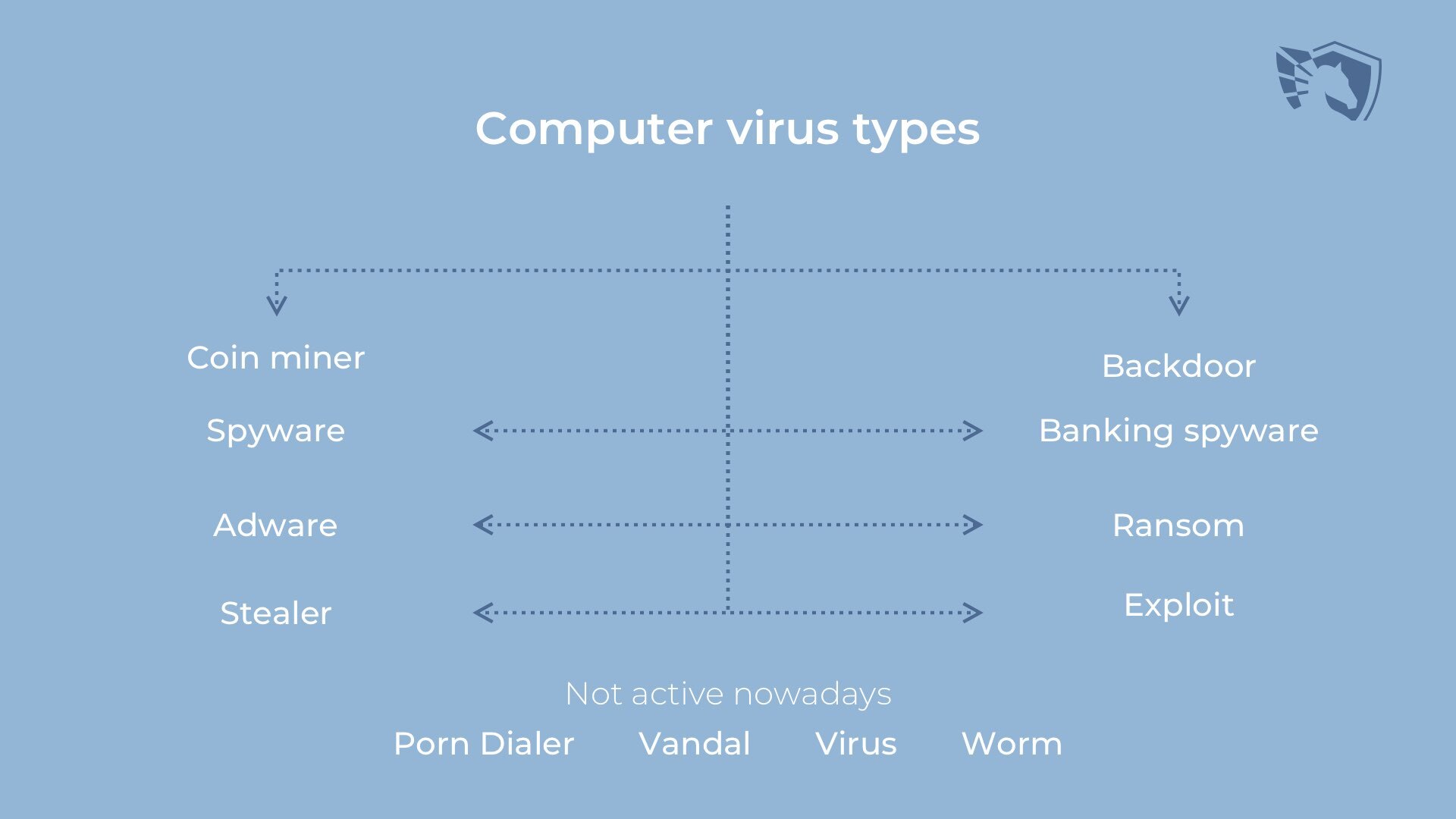
Backdoor viruses: silent and sly
It is a computer virus that allows the fraudster access to your computer without your permission. This software is usually used to create botnets – zombie computer network that does what crooks want. Inflating the polls on the websites, DDoS attacks, email spamming – all these things are not pleasant. Sometimes, backdoors are used as a combination of downloader and spyware.
Short reference about botnets
The term “botnet” is used to refer to a large collection of internet-connected devices – mainly PCs. You can call them minions because these computers are so easily used. They perform the tasks of other computers. Internet-connected TVs and routers are just about as easy. But an easy thing to forget is that bots are usually infected with malicious software to ensure the continuous distribution of new malware. You can use a botnet to send spam emails, perform DDoS attacks, and fake login sessions. It is possible to gain access to other devices or control their activity. However, all this is very expensive and dangerous – and it often requires a lot of human-powered labor.
Downloader malware: mitosis in the computer virus world.
Downloaders do exactly what is supposed by their name. The software is often used to download other viruses – or to manipulate your internet usage. If you see a message or banner in your browser – it might be downloader malware trying to get a connection from your computer and perform a malicious operation. Downloader viruses weaken your system by stopping security tools and modifying the registry and networking settings.
Having the downloader malware on your computer means having a chance to get any malware on your computer – including ransomware or vandal viruses.
Spyware. Your data is not only yours
Spyware is a computer virus that spies on you and your system. It generally collects personal data like contacts, cameras, and microphones and tracks your online activities. The purpose of spyware is to infect your computer and make money through selling your data – even the most sensitive. Crooks have no morality, so they will not even think about possible consequences for you.
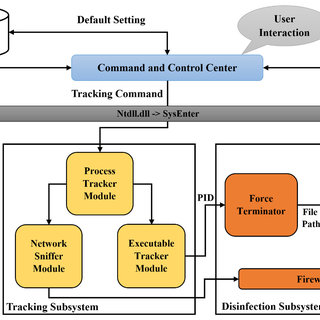
Spyware usually gives the full information about the infected computer to the fraudster who controls it. It collects even your PC configurations – that information can be valuable, too. At all, spyware looks like malware for massive attacks – but it is also used precisely against certain persons. Pegasus Spyware is a perfect example of one.
Stealer: spyware’s bro
Stealers are sometimes classified as a sub-type of spyware. From a certain point of view, they do not have a lot of differences from spyware, but deep dive into their actions points to significant distinguishes. While spyware collects all possible information about your system and you personally, the stealer aims at passwords, conversation logs, or even files. Stealers are often guests in cyberattacks on corporations – they ease network hacking and allow cyber criminals to get the most valuable files.
Keylogger malware – keep your fingers on the keyboard
Keylogger is a type of spyware that listens in on your keystrokes and provides some interesting information about your internet activity to the cybercriminal. It is effortless – it does not infect your computer with viruses but sits quietly in your computer until you need it to monitor a specific activity. For example, it records all the letters typed on your keyboard and sends them to a cybercriminal server to install the malware on your computer.
Adware – look at this banner!
Adware programs are a kind of programs that contain advertisements, tracking cookies, or links to online ads. This program is usually downloaded through a link in emails or by clicking on a pop-up window. Usually, adware programs do not have a very significant effect on your computer performance or your privacy. However, there are times when their effect on your computer is more severe – for example, when your browser crashes, a pop-up window with an advertisement appears on your screen, or they slow down your browser and decrease your battery life.
Browser hijackers
These viruses are brother-in-arms with adware. Browser hijackers are malicious programs that completely alter your browser settings to spy on you and show you advertisements. To do so, hijackers usually change your browser settings or infect it with viruses. One more typical symptom of browser hijacker activity is search query redirections – instead of Google, you will see the search results in Bing, Yahoo, or even Mail.ru.
Ransomware – the most dangerous computer virus
Ransomware is a computer virus that encrypts your personal files and asks you to pay a ransom for their decryption. These viruses do not only make your files inaccessible but can also make your files permanently inaccessible. Due to the extreme toughness of the encryption key of some of the ransomware examples, there is no way to decrypt the files. In this case, you have no choice but to keep your files ciphered. Paying the ransom is always a bad idea.
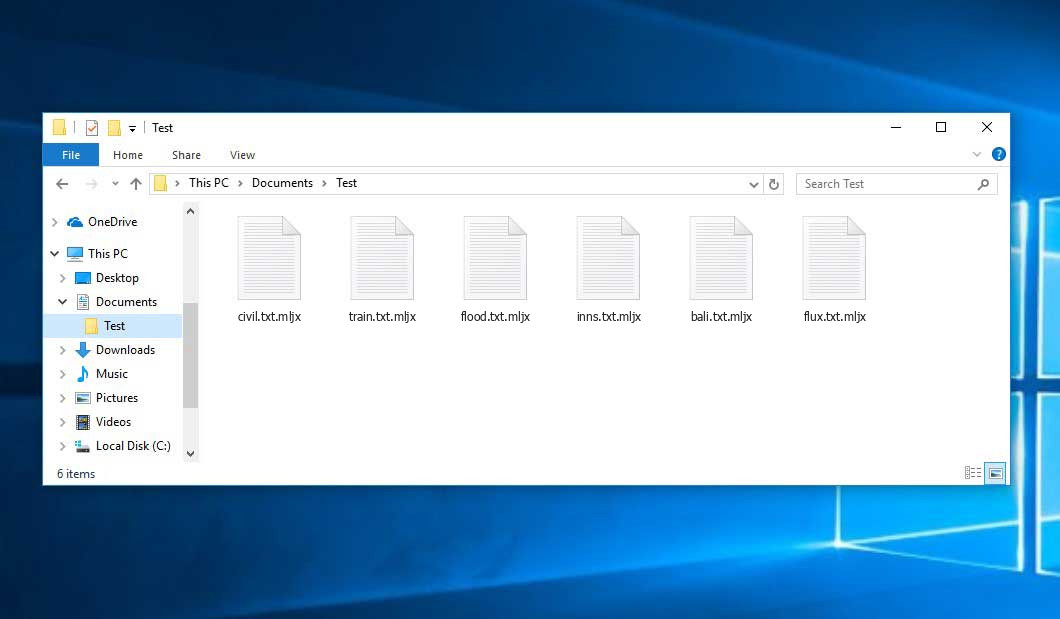
Nowadays, ransomware is the biggest worry of companies. It is used for large-scale corporate attacks, but some ransomware families aim at individuals. More than 50,000 ransomware attacks occurred daily in 2017.
Exploit virus. Turn your system ahead of cheese
Exploit malware is a small malicious thing that appears in your computer with a single final target – inject other malware. It usually contains some functionality of a downloader virus but does completely different things to your system. It searches for security breaches in the software you have on your disk. When it finds one, it reports it to the crooks. Then, burglars prepare the malware that exploits these breaches to infect the computer network. Yes, it is generally used in attacks on corporations.
What is an exploit?
An exploit is a small part of a software program that becomes exploitable or “jailbroken.” An exploit allows you to modify the behavior of the program. When you use the program, it offers you certain access keys for setting up configurations or displaying different features. Exploit programs offer a way to hack the program and gain full access to its contents. However, exploit programs cannot steal data – they only set up access keys.
Coin mining malware
Coin Miner virus mine cryptocurrencies using your hardware – in particular, Monero and DarkCoin. Coin miner viruses compromise your computer’s graphics card to improve the speed of mining algorithms. There are no known coins that coin miners mine. The problem with using coin miners is that they are very slow – sometimes they use up to 80% percent of your computer’s resources – and also risk overheating.
How to prevent computer virus injection?
To avoid being infected with such viruses – it’s important to have the newest security system on your computer and to be careful with your privacy settings in social networks. You should always be vigilant and check for new malware attacks on your computer. Also, if you are using a public WiFi network – use a trusted and secure one. For example, if you go to Starbucks, use a public library – instead of waiting for a free connection – or use a virtual private network.
Safeguarding yourself against viruses is not an easy job. But it’s worth it. Taking the right measures and knowing how to avoid being a victim of a virus is the best way to protect yourself from all these destructive viruses. And the security system, exactly – a good anti-malware program – must be ahead of everything you do to make your system secure.
