The catalog of add-ons for Firefox (AMO) noted a massive publication of malicious add-ons hiding behind well-known projects.
Researcher Martin Brinkmann discovered and it tested on examples.
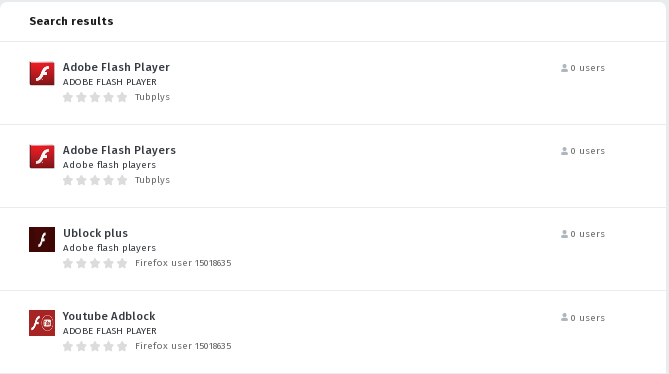
For instance, in the catalogue posted malware add-ons “Adobe Flash Player“, “ublock origin Pro“, “Adblock Flash Player” etc.As these add-ons are removed from the catalog, the attackers immediately create a new account and substitute them with new malware add-ons.
For example, a few hours ago, the Firefox user account 15018635 was created, under which the add-ons “Youtube Adblock“, “Ublock plus“, “Adblock Plus 2019” located. Apparently, the description of the additions formed to ensure that they are displayed in the top on such searching queries as “Adobe Flash Player” and “Adobe Flash“.
When you install an add-on, you are asked for permissions to access all the data on the sites you are browsing. In the process of work, the keylogger is launched, which sends information about the filling out of forms and the installed cookies to theridgeatdanbury.com host.

“When you download the extensions, you may notice that the name of the extension does not necessarily match the downloaded file name. The download if ublock origin pro returned a adpbe_flash_player-1.1-fx.xpi file”, — writes Martin Brinkmann in ghacks.net portal.
The script code inside add-ons is slightly different, but the malicious actions they perform are obvious and not hidden.
Probably, absence of application of techniques for hiding malicious activity and extremely simple code make it possible to bypass the automated system of preliminary review of add-ons. At the same time, it is not clear how the fact of the explicit and non-hidden sending of data from the add-on to an external host can be ignored during an automated check.
Recalling, Mozilla argues that introduction of a digital signature check will block the distribution of malicious and spyware add-ons.
Some add-on developers do not agree with this position and believe that the mandatory digital signature verification mechanism only creates difficulties for developers and leads to increase in the time of communicating corrective releases to users without affecting security.
Many trivial and obvious techniques of bypassing system of automated verification of add-ons allow secretly inserting malicious code. For example, by forming an operation on the fly by connecting several lines and executing the resulting string by calling eval.
Read also: [Makeseparatebestappclicks.top] fake Adobe Flash Player update alert removal
Mozilla’s position narrows to the fact that most authors of malicious add-ons are quite lazy and will not resort to similar techniques to hide malicious activity.
In this manual check is not completely abolished, and selectively carried out for already placed additions. Supplements for manual verification are selected based on the calculated risk factors.
Source: https://www.ghacks.net




