Specialists from Guardicore Labs reported about discovery of the malware Nansh0u, and some Chinese hacking group is responsible for it.
The attackers compromise MS-SQL and PHPMyAdmin servers around the world, infect them with a cryptocurrency miner, and install rootkits that protect the miner from deletion.“Breached machines include over 50,000 servers belonging to companies in the healthcare, telecommunications, media and IT sectors”, — report Guardicore Labs researchers.
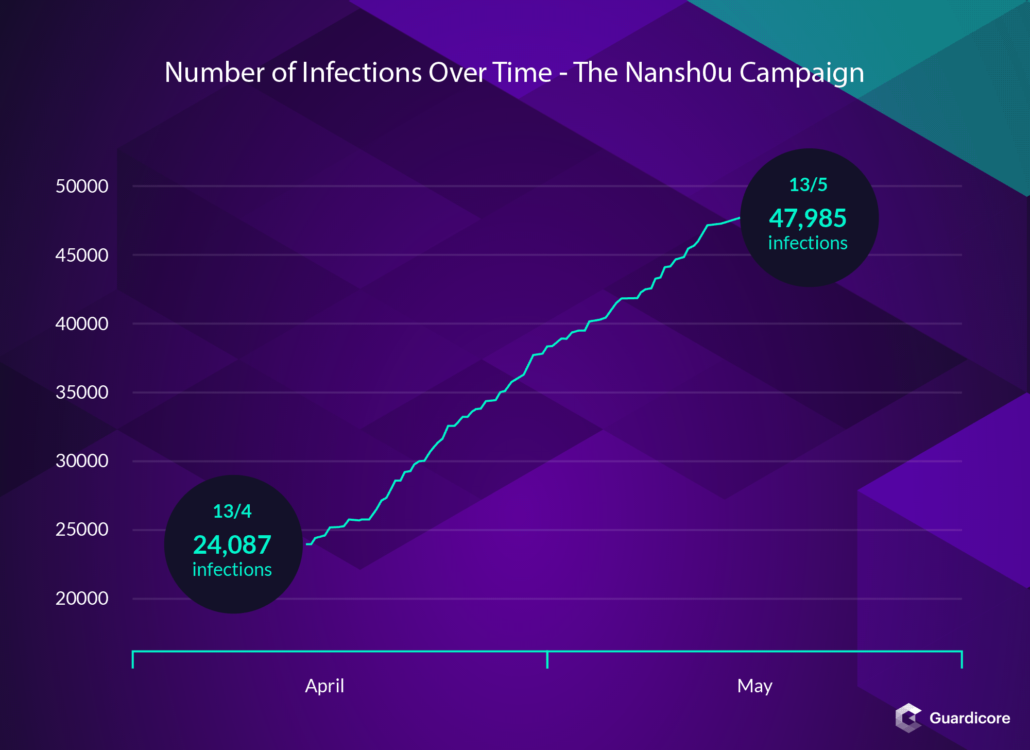
According to experts, the campaign was launched on February 26, 2019, but was discovered only in April, when experts noticed that criminals spread 20 different payloads hosted by various providers.
“The Nansh0u campaign is not a typical crypto-miner attack. It uses techniques often seen in APTs such as fake certificates and privilege escalation exploits”, — commented attacks in Guardicore Labs.
The initial phase of the attacks is quite simple: attackers find poorly configured and vulnerable Windows MS-SQL and PHPMyAdmin servers on the network, and using normal brute-force and port scanning penetrate the system, as a rule, with high privileges.
Next, attackers execute a series of MS-SQL commands to download the malicious payload from the remote server. After that, the malware (and it is the TurtleCoin cryptocurrency miner) runs with the SYSTEM privileges – for this, hackers apply the known vulnerability CVE-2014-4113, which allows elevating rights.
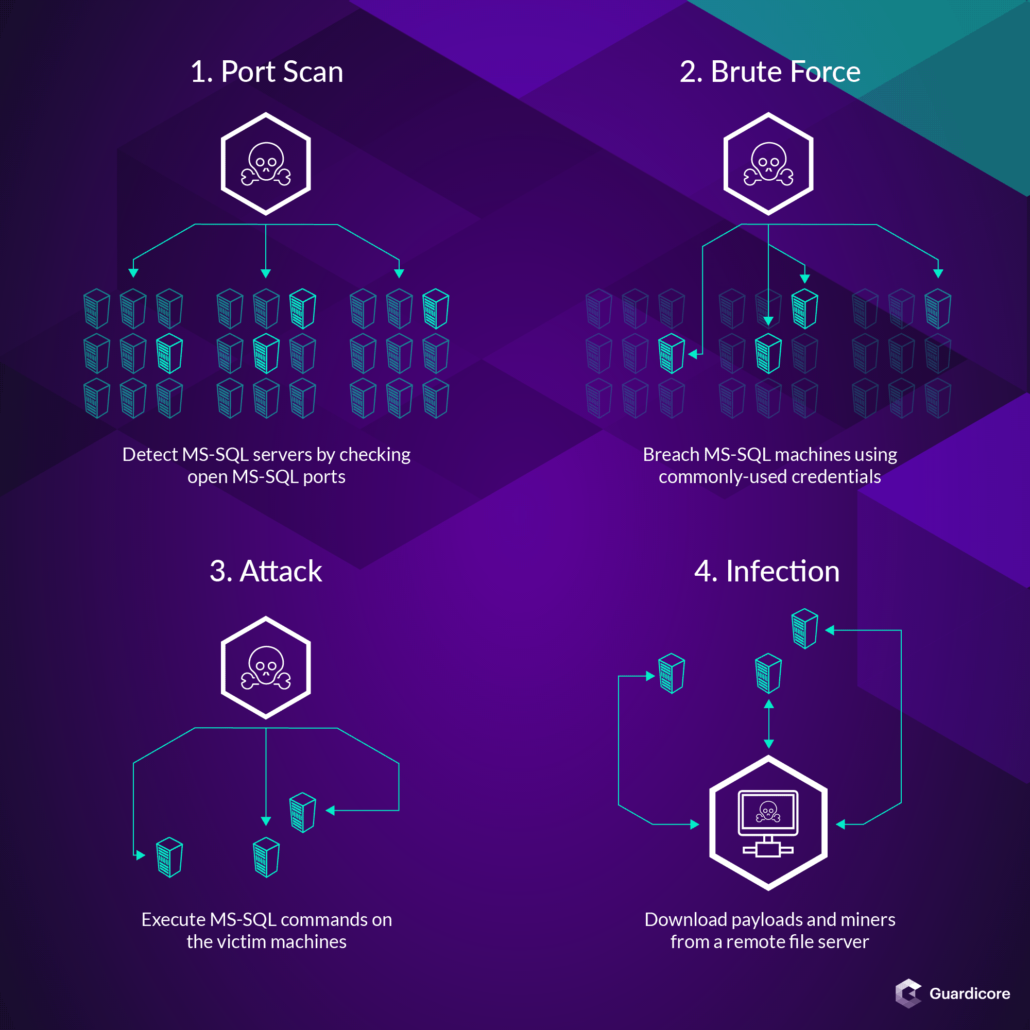
In addition, to protect their malware from removal and ensure the stability of the infection, attackers use a kernel-mode rootkit, signed by a certificate from the Verisign certification center. Currently, the certificate has already expired, besides, it was originally issued by the fake Chinese company Hangzhou Hootian Network Technology.
“This campaign was clearly engineered from the phase of IPs scan until the infection of victim machines and mining the crypto-coin. However, various typos and mistakes imply that this was not a thoroughly-tested operation”, — argue in Guardicore Labs.
Researchers also investigated attackers’ origin.
We can confidently say that Chinese attackers have operated this campaign. We base this hypothesis on the following observations:
1. The attacker chose to write their tools with EPL, a Chinese-based programming language.
2. Some of the file servers deployed for this campaign are HFSs in Chinese.
What enables this attack on Windows MS-SQL servers in the first place, is having weak usernames and passwords for authentication. As trivial as it may sound, having strong credentials is the difference between an infected and a clean machine.
Guardicore Labs experts have already published a list of compromise indicators, and wrote a special Powershell script that will help detect Nansh0u infection or its remnants.
Source: https://www.guardicore.com




