Physical Address
Lesya Kurbasa 7B
03194 Kyiv, Kyivska obl, Ukraine
Physical Address
Lesya Kurbasa 7B
03194 Kyiv, Kyivska obl, Ukraine
The cryptocurrency industry continues to attract not only legitimate investors and developers but also malicious actors seeking to exploit the complex and often confusing nature of blockchain technology. One such deceptive scheme is the fake “Solana L2 Presale” scam, which targets crypto enthusiasts by impersonating legitimate projects associated with the Solana blockchain. This comprehensive guide explains how the scam operates, provides detailed statistical analysis of cryptocurrency scams, and offers actionable guidance to protect your digital assets from similar threats.
| Threat Name | Solana L2 Presale Scam, Fake Solana Layer 2 Investment Scam |
| Type | Phishing, Cryptocurrency Scam, Social Engineering, Fraud |
| Target | Cryptocurrency investors, Solana ecosystem users, Crypto enthusiasts |
| Distribution Methods | Compromised websites, social media spam, rogue online ads, potentially unwanted applications |
| Known Domains | dashboard-solaxy.pages[.]dev (note: new domains constantly emerge) |
| Detection Names | CyRadar (Phishing), Emsisoft (Phishing), Netcraft (Malicious), Trustwave (Phishing), Webroot (Malicious) |
| Damage Level | Critical – Complete loss of cryptocurrency assets with no recovery possibility |
The Solana L2 Presale scam is a sophisticated phishing operation designed to steal cryptocurrency by tricking users into connecting their digital wallets to fraudulent websites. These scam sites impersonate legitimate Solana blockchain projects, creating a false sense of urgency around a supposed “Layer 2” solution presale event.
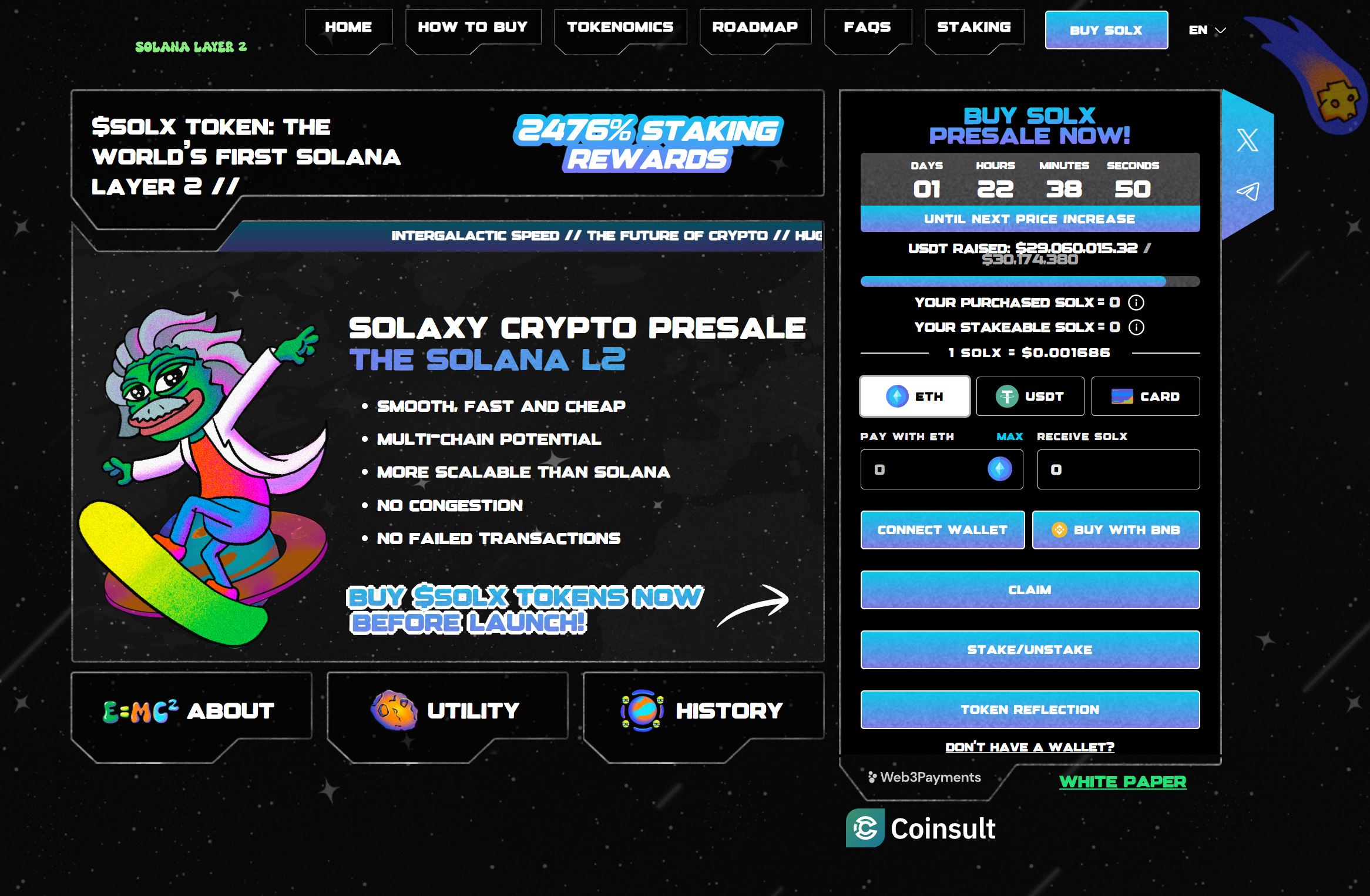
Important: This scam is in no way associated with the legitimate Solana blockchain (solana.com) or any authorized Solana ecosystem projects. Solana does not currently have what’s technically called a “Layer 2” solution in the same way Ethereum does, making any “Solana L2” presale inherently suspicious.
When victims attempt to participate in these fake presale events, they are prompted to connect their cryptocurrency wallets by entering sensitive access credentials. Once scammers obtain these credentials, they gain complete access to the victim’s digital assets and can transfer all funds to their own wallets – transactions that are irreversible due to the fundamental nature of blockchain technology.
Source: Analysis of cryptocurrency phishing techniques based on CISA cryptojacking and blockchain threat analysis
The Solana L2 Presale scam employs several technical mechanisms to appear legitimate while extracting valuable credentials from victims:
Scammers register domains that mimic official Solana-related properties, often using variations such as:
The fraudulent websites typically utilize sophisticated cloning methods:
The scam uses several methods to steal cryptocurrency wallet credentials:
To avoid detection and maximize effectiveness, these scams implement various evasion techniques:
Understanding the scale and impact of cryptocurrency scams provides important context for assessing the risk posed by schemes like the fake Solana L2 Presale:
Source: Data compiled from FTC Consumer Protection Data Spotlight, Chainalysis 2023 Crypto Crime Report, and FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center reports
Identifying cryptocurrency scams before becoming a victim requires vigilance and awareness of common red flags. Here are key indicators specific to the Solana L2 Presale scam and similar cryptocurrency frauds:
For those wishing to conduct more thorough due diligence:
# Command to check domain registration informationwhois dashboard-solaxy.pages.dev# Command to search for mentions of a domain in security databasescurl -s https://urlscan.io/api/v1/search/?q=dashboard-solaxy.pages.dev | jq . |
Protecting yourself from the Solana L2 Presale scam and similar cryptocurrency frauds requires implementing several security practices:
If you believe you’ve fallen victim to the Solana L2 Presale scam or a similar cryptocurrency fraud:
In addition to crypto-specific precautions, maintaining general system security is essential for protecting your digital assets:
Some cryptocurrency scams deploy malware that can monitor clipboard activities and replace crypto addresses with the scammer’s address when you copy-paste. Regularly scan your system with reputable security software:
The Solana L2 Presale scam is just one of many similar cryptocurrency frauds. Be vigilant about these related scams:
No. Unlike Ethereum, which has various Layer 2 scaling solutions (such as Optimism, Arbitrum, and Polygon), Solana’s architecture is fundamentally different and doesn’t utilize the same Layer 2 approach. Solana is designed for high throughput at the base layer. Any website claiming to offer a “Solana L2 Presale” is almost certainly fraudulent. Solana does have projects working on scalability and interoperability solutions, but these aren’t technically “Layer 2” solutions in the same sense as Ethereum’s ecosystem. Always verify any investment opportunity through Solana’s official channels (solana.com) and established cryptocurrency news sources.
Cryptocurrency scammers typically employ sophisticated methods to convert stolen digital assets into cash while avoiding detection. First, they often transfer stolen funds through multiple wallets to obscure the trail, a process known as “chain-hopping.” They then use decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to swap between different cryptocurrencies, making the trail even harder to follow. Next, they may employ cryptocurrency mixing or tumbling services to further conceal the origin of the funds. Finally, they convert cryptocurrencies to fiat either through exchanges with weak KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements, peer-to-peer platforms, or by purchasing gift cards and luxury goods that can be resold. Some sophisticated operations also utilize money mules—individuals who knowingly or unknowingly help transfer stolen funds—or leverage overseas exchanges in jurisdictions with limited regulatory oversight.
No, blockchain transactions cannot be reversed once they’ve been confirmed on the network. This immutability is a fundamental feature of blockchain technology and applies to all major cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana. Unlike traditional banking where institutions can reverse fraudulent transactions, there is no central authority that can undo or reverse cryptocurrency transactions. This is why prevention is so critical when it comes to cryptocurrency scams. Once your digital assets have been transferred to a scammer’s wallet, they are effectively gone. The only potential for recovery would be through law enforcement actions that might identify and prosecute the perpetrators, but even in these rare cases, recovery of assets is not guaranteed. This irreversibility is why cryptocurrency users must exercise extreme caution and verify the legitimacy of any platform or service before connecting their wallets or sending funds.
Verifying a cryptocurrency project’s legitimacy requires multi-faceted due diligence. Start by checking if the project has a professional website with comprehensive documentation, including a detailed whitepaper explaining the technology, use cases, and tokenomics. Examine the team behind the project—legitimate projects typically have transparent teams with verifiable backgrounds and expertise in blockchain or relevant fields. Investigate the project’s code repository on platforms like GitHub to assess development activity and code quality. Look for security audits conducted by reputable firms like CertiK, Trail of Bits, or OpenZeppelin. Review the project’s presence on social media and community platforms like Discord or Telegram, noting the quality of discussion and team engagement. Check trusted cryptocurrency news sources and review platforms for mentions and assessments. Finally, verify if the token is listed on reputable exchanges and trackers like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko, though note that listing alone doesn’t guarantee legitimacy. Always approach with skepticism any project promising unrealistic returns or using high-pressure sales tactics.
Cryptocurrency scams are promoted through various sophisticated channels to reach potential victims. Social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok are primary vectors, where scammers create fake accounts impersonating well-known figures, cryptocurrency projects, or exchanges. They also compromise existing accounts with large followings to promote scams. Direct messaging is another common approach, with scammers sending unsolicited messages through platforms like Telegram, Discord, WhatsApp, or email, often initiating conversations about investment opportunities. Many scams spread through paid online advertisements on search engines and websites, sometimes bypassing ad network security measures. Some scammers create fake news articles or “sponsored content” that appear legitimate but lead to fraudulent opportunities. Phishing emails that mimic communications from legitimate cryptocurrency services are also prevalent. Additionally, airdrop scams target users by promising free tokens in exchange for connecting wallets or providing sensitive information. The most sophisticated operations may even list fraudulent tokens on decentralized exchanges with artificial trading volume to create an illusion of legitimacy and activity.
The Solana L2 Presale scam represents a sophisticated but increasingly common threat in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. By impersonating legitimate projects and exploiting both technical naivety and investment FOMO (fear of missing out), these scams have successfully stolen billions of dollars worth of digital assets from victims worldwide.
As cryptocurrency adoption continues to grow, we can expect scammers to develop increasingly sophisticated techniques. The irreversible nature of blockchain transactions makes prevention and education the most effective defenses against these threats.
By implementing strong security practices, conducting thorough research before any investment, and staying informed about the latest scam techniques, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cryptocurrency fraud. Remember that legitimate investment opportunities don’t require urgency or secrecy—take your time to verify before you trust.
For ongoing protection against cryptocurrency scams and other digital threats, maintain good cybersecurity hygiene and consider using comprehensive security software like Trojan Killer, which can detect and remove crypto-stealing malware and other security threats before they compromise your digital assets.